
Gogo’s testbed, a Boeing 737-500 (reg. no. N321GG) dubbed the “Jimmy Ray”
You might have heard of Gogo, that company that lets you check Facebook watch Youtube be productive while you’re 30,000 feet in the air. And you might have been one of those who sighed loudly when your cat video kept pausing and buffering.
From the power user traveling for work, to the new user who will update their status to, “I’m posting this from the plane!”, most can agree that data speeds inflight are nowhere near what we’re used to on the ground. We take connectivity on land for granted, but in the air the concept is still novel and exciting (before it disappoints us multiple times with the infinite spinning “Loading…” circle).
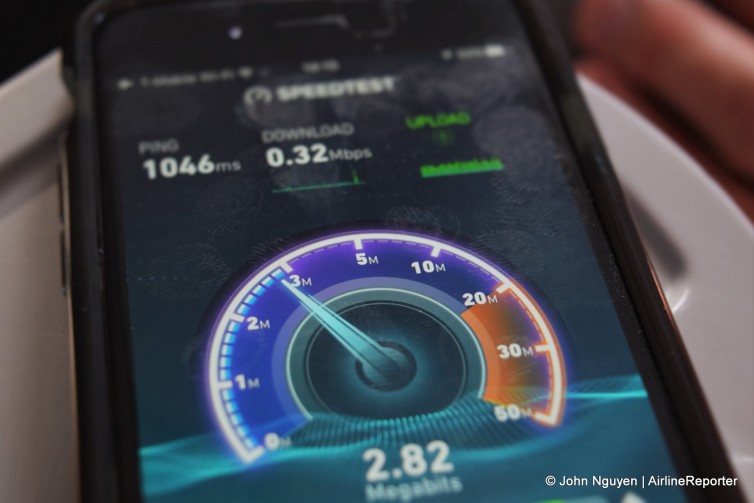

An #AvGeek testing Gogo’s speed
Gogo wants you to have really, really fast Internet, and they invited AirlineReporter to come check out their new headquarters in Chicago’s Loop, as well as to experience their test bed in action (or in #AvGeek-speak, fly on their private, tricked out Boeing 737-500). Can Internet access actually get better, and what does it mean for the regular passenger?

Inside the Gogo Network Operations Center – Photo: Blaine Nickeson | AirlineReporter
As a frequent flier, the novelty of in-flight internet has (mostly) worn off for me. After a full day of presentations, tours, and demonstrations at Gogo, I can promise you that I’ll never take it for granted again. Gogo invited me as part of a group of journalists from both the travel and tech sectors to take part in a day-long “all access” event at their headquarters, near Chicago O’Hare airport.
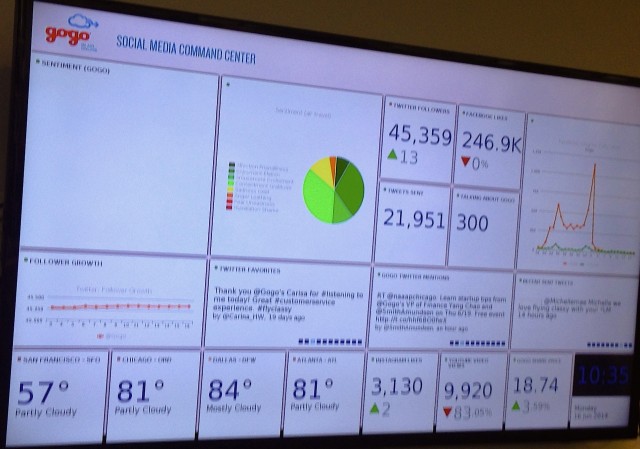
Gogo’s “Social Media Command Center” – Photo: Blaine Nickeson | AirlineReporter
Gogo is the largest provider of in-flight connectivity, with over 2,000 commercial planes equipped and 6,000 business jets. Originally known as Aircell (and a lot of equipment I saw still had that name on it), the company was founded in 1991 to provide in-flight telephone access. In 2008, Gogo launched in-flight broadband on their first commercial flight, and our lives as fliers has never been the same.

Qantas Airbus A380 landing at LAX.
Getting on a plane with-in the US that offers in-flight internet is not that rare anymore. Many airlines have their entire fleet outfitted and others are still in process. For some, having access to the internet for a flight that might only last a few hours is not a huge perk — yet, there is surely more demand for flights that are longer. Since most US-based in-flight internet makes use of cell towers on the ground, the service is not available for international flights. Satellite based systems are heavier, cost more and take longer to install. Because of this, we have not yet seen a many airlines that offer Wi-Fi on longer, international flights.
Even though there have been quite a few airlines that have announced their intent to provide satellite internet service, many have not followed through for one reason or another. One airline that is moving forward with long-haul internet is Qantas.
Qantas Airlines decided to use OnAir as their service provider and they currently have six of their Airbus A380 aircraft flying between Australia and the US configured to offer Wi-Fi on an eight week trial.
’œThe eight-week trial will give customers the opportunity to access the Internet in exactly the same way as a terrestrial Wi-Fi hotspot in which customers can pay with their credit card and surf the Internet, including the use of email,’ Qantas Executive Manager Customer Experience, Alison Webster, said.
Since this is a trial run, only passengers in premium cabins (first and business) will have the opportunity to try out the OnAir Wi-Fi. After the two months is up, Qantas, “will assess opportunities for the long-term application of Internet capabilities across its A380 fleet.”
Australian Business Traveler (AusBT) was able to get a first hand account on how the new Wi-Fi service works. They tell the story of Andrew Hazelton, who flew on February 29th and was given 35MB of bandwidth to use during his flight. That is not much, especially for a long flight and Hazelton told AusBT that he used all of his bandwidth quickly and he was not super impressed by the slow speed of the service. Of course, this is just a trial period and it is hoped that speeds will improve with time.
During the trial, the internet is free for first class and business class passengers and Qantas and OnAir are in process of figuring out how much they might want to charge for the service, if the trials are successful.
Besides testing satellite internet, Qantas is also working with aircraft based entertainment, accessed through Wi-Fi. The new service, called Q Streaming, allows customer to wirelessly connect to computers on the aircraft to access an array of in-flight entertainment options.
See a video played on the Q Streaming aircraft to let passengers know they are on a special aircraft
Passengers have high expectations and I feel that in the next year or so we will see more airlines adding the ability to access Wi-Fi on international flights. It might not be the best quality of service, but with additional development, we will all see quicker and cheaper options.
Image: Jeremy Dwyer-Lindgren

That bump on the back of the Southwest Boeing 737 gives Row44 internet to the aircraft.
Recently I got a call on my phone where I didn’t recognize the number, so I decided not to answer. Then they called again. Okay, fine — it might be something important so I answered and it turned out to be my friend Nick. Wait a second; #1 why is he calling with a number I do not know and #2 he is flying on Delta Air Lines from Minneapolis (MSP) to Seattle (SEA), how is that possible? Even though airlines and internet providers have tried to ban talking via phones on airliners, there are still pretty easy ways to get around it.
Earlier Nick and I had been talking about VOIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol) and I was explaining how you cannot have a phone conversation while flying — he was all too happy to prove me wrong. This is by no means a “how-to” story and I am not going to explain how he did it, since I am against people talking via their phone on planes. However, I can say it was nothing complicated and anyone with a smart phone could and an internet connection could replicate it.
So, it was possible to use GoGo Wi-Fi (internet provider on Delta and other airlines) to talk on the phone and I wondered what policies airlines and internet providers had in place to stop passengers from doing things they should not (phones, porn, etc).
I first spoke with Steven Nolan with GoGo Communications and he explained, “We do restrict VOIP services and at the request of our airline partners, we also restrict access to some web sites.” One of the big challengers is technology is always changing and it can be difficult to know all the “bad” sites and smart phone applications. What happens when someone, like Nick, finds a loophole? Well, talking to multiple airlines, this doesn’t seem to be a big problem.
Virgin America’s Abby Lunardini explained that they block VOIP and have not had any major issues with passengers finding their way around it. Alaska Airlines also bans VOIP for passengers on their GoGo internet. Even though they haven’t had a lot of issues, the flight crew are trained to enforce the airline’s policy. “Should a customer get around the VOIP blocking, our flight attendants would be prepared to enforce our policy which prohibits voice calls of any kind inflight,” Alaska Airline’s Bobbie Egan explained to AirlineReporter.com.
Row44, another airline internet provider, that can be found on Southwest Airlines and Norwegian Air Shuttle helps airlines in similar ways. They provide airlines software that allows them to choose what sites they want to block. “We allow our airline partners to decide whether to use this option and which sites to block,” Row 44’s chief commercial officer, Howard Lefkowitz explained over email. Row44’s airline customers are easily able to add new sites that are deemed to be a problem since new technologies are always emerging. “The back-end system supporting Row 44’s broadband entertainment platform adapts quickly and can immediately add new sites (VoIP services or other types of websites) to the list of blocked content in-flight. But this will be a decision for our airline partners.”
So does this become a game to beat the internet providers and the airlines? No, at least it shouldn’t. Public opinion in the US is pretty split on allowing in-flight conversations. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) bans cell phone usage in the US and it is still against airline policy. Nick was a good passenger and kept our conversation short, even though he supports passengers being allowed to talk on their cell phones on a plane.
What are your thoughts? Other airlines around the globe let passengers talk on their cell phones with little to no issues are Americans ready?
Image: gTarded

Two will enter, one will leave. Some will have Wi-Fi.
United has announced today that Continental intends to add Wi-Fi to 200 of their Boeing 737 and 757 aircraft. It is not officially, official that this will happen, but I would imagine it will go through.
If you get confused on who and what United and Continental Airlines are right now, you are not alone. Although they will be merging, they are still two separate airlines. This gets more confusing since they have started to re-paint planes and doing joint announcements.
Add to the confusion that currently, United flies fourteen aircraft with Wi-Fi already on their Premium Service (PS). 13 of those aircraft are using Go-Go Inflight Wi-Fi and one is using Row 44. The Continental aircraft will be using LiveTV’s ViaSat-1 satellite internet. Those are a lot of different providers and I would imagine as the merger settles down, the new United will be looking at which service package they would want to provide to the entire fleet. Since the new United has so many international destinations, it makes sense for them to look at using a satellite provider like Row44 or LiveTV.
Becoming the world’s largest airline is not easy. There are a lot of things that still need to be dealt with to make sure the new United has a consistent brand.Time is of the essence since the new United doesn’t want to alienate loyal customers for both airlines during the transition.
To learn a bit more, check out my story on AOL Travel News.






